Table of Contents
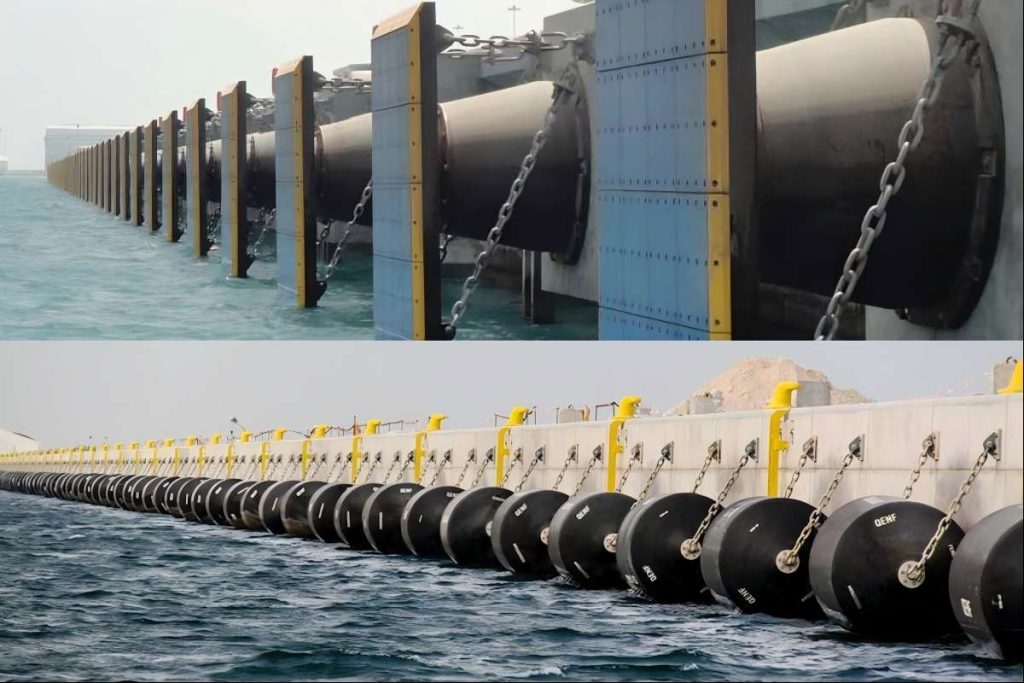
Marine fenders are protective devices used to absorb the kinetic energy generated by vessels when docking or mooring, preventing damage to both the vessel and the berthing structure. Typically made from rubber, foam, or air-filled materials, fenders act as a cushion between the ship and the dock or another vessel. They serve as a critical line of defense against impact forces, especially during berthing in harsh conditions or when vessels make contact with hard surfaces such as piers, quays, or other ships.
Selecting the right marine fender is crucial for ensuring the safety of vessels, crew, and port infrastructure. Proper fender selection considers factors like the size and type of the vessel, the environmental conditions, and the type of berthing structure. Choosing the correct fender type can mitigate the impact of docking, reducing the risk of damage and ensuring the longevity of both the vessel and the berthing structure.
W Type Rubber Fender
Common Types of Marine Fenders
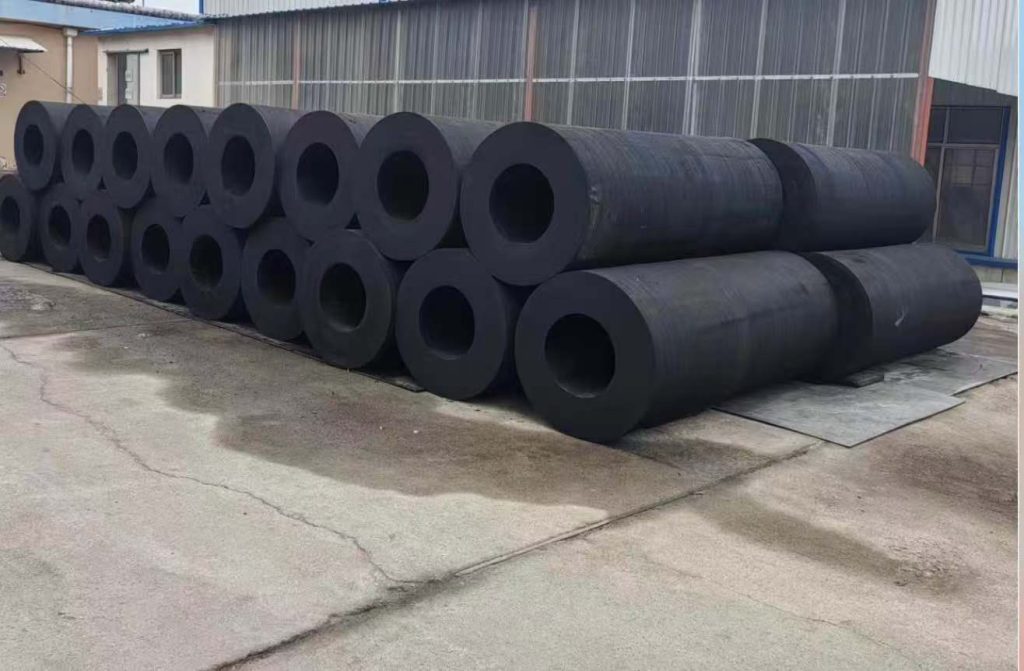
Solid Rubber Fenders
| Type of Fender | Description |
| Super Arch Fender | Renowned for its exceptional capacity to absorb impact energy, designed for safeguarding large vessels under rigorous berthing conditions. The distinctive arch profile optimizes protection against forceful impact during docking. Its robust construction ensures reliable performance and longevity in demanding marine environments. |
| D Type Fender | Characterized by a versatile D-shaped cross-section, this fender excels in energy absorption and resistance to abrasive forces. Suitable for a wide range of marine applications, including commercial ports and offshore platforms. Its balanced design provides effective protection while minimizing reaction forces. |
| Cylindrical Fender | Simple yet efficient cylindrical shape, well-suited for smaller vessels in less demanding berthing conditions. Provides consistent protective surface along its length for reliable impact dissipation. The straightforward design facilitates easy installation and maintenance. |
| Cone Fender | Designed to withstand high impact forces with a tapered profile that optimizes energy absorption, reducing the risk of damage to vessels and berthing structures. Often used in combination with other fender types for comprehensive protection. |
| Cell Fender | Constructed with internal rubber cells, offering outstanding energy absorption and durability. The cellular structure enhances resilience to impact, making it ideal for harsh marine environments with extreme weather and heavy vessel traffic. Known for its long service life and low maintenance requirements. |
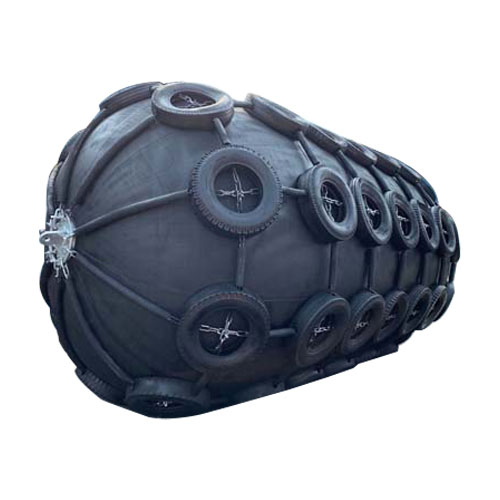
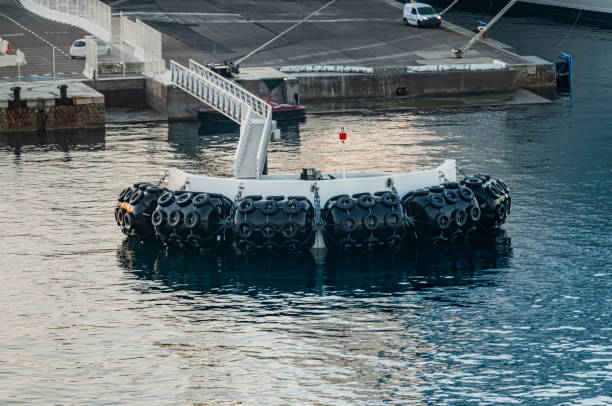
Pneumatic Fenders
- Pneumatic Fenders: Also known as Yokohama Fender, as a preeminent choice for floating fender applications, the pneumatic fender employs compressed air to deliver exceptional energy absorption while exerting minimal reaction forces. Its versatile design renders it suitable for a broad spectrum of marine operations, including critical ship-to-ship transfer scenarios. The fender’s ability to conform to vessel movement ensures optimal protection, mitigating the risk of damage to both vessels involved.
Pneumatic Fender
6 Key Factors in Marine Fenders Selection
Selecting the optimal fender for a specific marine application necessitates careful consideration of several critical factors:
1. Vessel Size and Type
Considerations for Large vs. Small Vessels:
- Large Vessels: Require heavy-duty fenders with high energy absorption and durability to withstand the forces exerted during berthing.
- Smaller Vessels: Need more flexible and adaptable fenders that can be easily positioned and maintained, offering adequate protection without the need for excessive energy absorption.

2. Berthing Conditions
The conditions under which a vessel docks significantly influence fender selection. High-speed docking or docking at sharp angles increases the impact force, necessitating fenders with superior energy absorption capabilities.
Open-Sea Berthing vs. Sheltered Ports:
- Open-Sea Berthing: Requires fenders that can withstand harsh conditions such as strong currents and waves, often demanding more robust and larger fenders.
- Sheltered Ports: Generally involve more controlled conditions, allowing for the use of fenders that prioritize ease of installation and maintenance, with less emphasis on extreme impact absorption.
3. Environmental Factors
- Influence of Weather Conditions: Weather elements such as waves, tides, and wind can affect how vessels dock and the type of fender required.
- Durability in Extreme Environments: In areas with extreme climates, such as the Arctic or tropics, fenders must be made from materials that can withstand temperature fluctuations, UV exposure, and other environmental stresses. For instance, rubber fenders might need to resist cracking in cold climates or degradation from intense UV exposure in tropical areas.
4. Installation and Maintenance
- Fenders that are easy to install and require minimal maintenance are more cost-effective in the long run, reducing downtime and operational costs. If you want to know how to install rubber fenders correctly, you can read this article: How to Replace and Install Rubber Fenders?
- Fenders made from durable materials like high-quality rubber or those designed with simple shapes (e.g., cylindrical fenders) often require less upkeep and can be easily replaced or repaired, contributing to overall operational efficiency.

5. Energy Absorption and Reaction Force
- The primary function of a fender is to absorb the kinetic energy generated during docking, preventing damage to the vessel and the berthing structure. High energy absorption is particularly important for large vessels and high-speed docking scenarios.
- While absorbing energy, fenders should also minimize the reaction force exerted on the vessel and the dock. This balance ensures that neither the vessel nor the docking structure sustains damage, maintaining safety and integrity during berthing.
6. Cost Considerations
- The initial investment in high-quality fenders can lead to significant savings over time due to reduced maintenance costs, fewer repairs, and longer service life.
- While lower-cost fenders may seem appealing initially, they may not provide the necessary protection or durability, leading to higher long-term costs. It’s crucial to consider both the upfront expense and the long-term performance and durability of the fender.
Choose The Right Marine Fenders
Proper fender selection is not just about choosing a product, it requires a comprehensive analysis of all factors that could impact the safety and efficiency of marine operations. A well-chosen fender enhances the protection of vessels and berthing structures, reduces the risk of damage, and contributes to the overall success of marine operations.
Stakeholders in marine operations should prioritize fender selection as a critical aspect of their safety and operational planning. By carefully evaluating the specific needs of their vessels and berthing conditions, they can ensure the safety of their assets, reduce long-term maintenance costs, and maintain smooth and efficient operations in all marine environments.