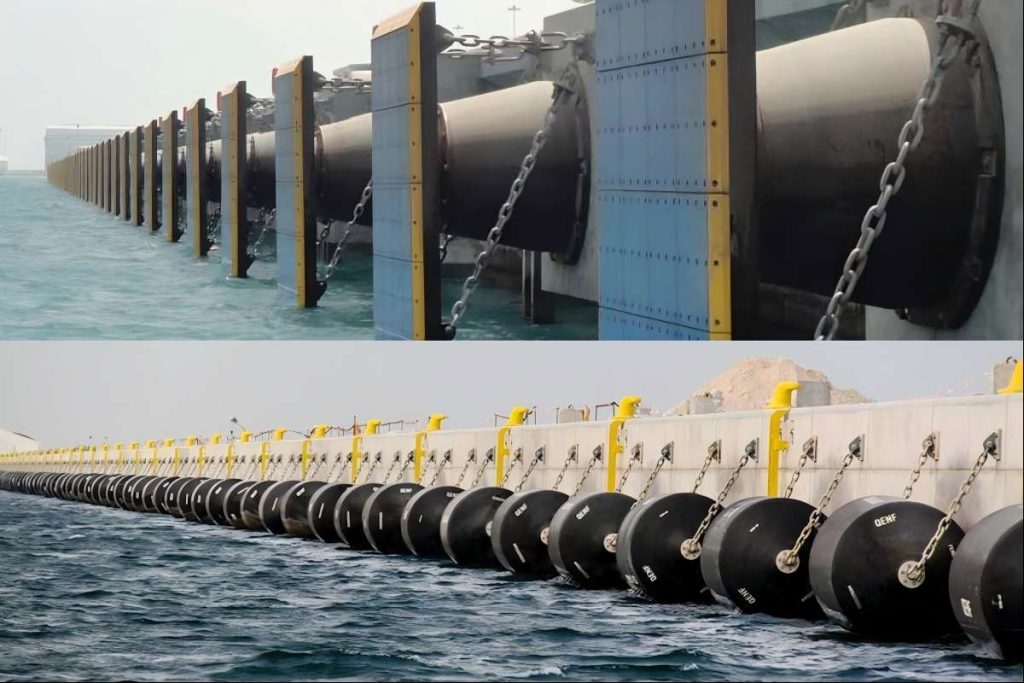
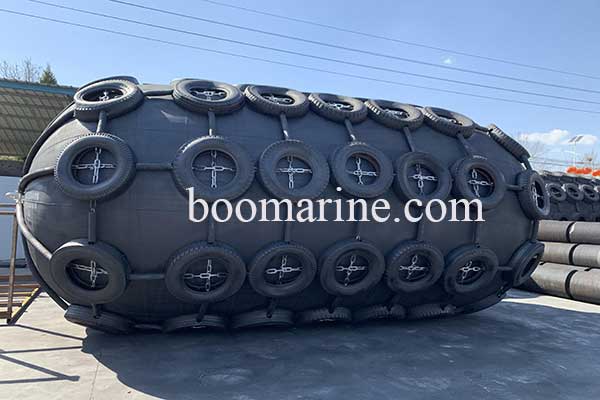
Yokohama fender, also known as pneumatic fender, is a common floating fender. It mainly uses air as the medium and uses compressed air to absorb impact energy. It makes the ship more flexible and soft when berthing, so as to achieve the effect of anti-collision.

Basic Composition of Yokohama Pneumatic Fenders
The Yokohama pneumatic fenders are made of synthetic cord reinforced rubber sheets with compressed air inside with an initial pressure of 50kpa or 80kpa, allowing them to float on the water and act as shock absorbers between the two boats. According to ISO17357-1:2014, the pneumatic fender consists of the following parts:
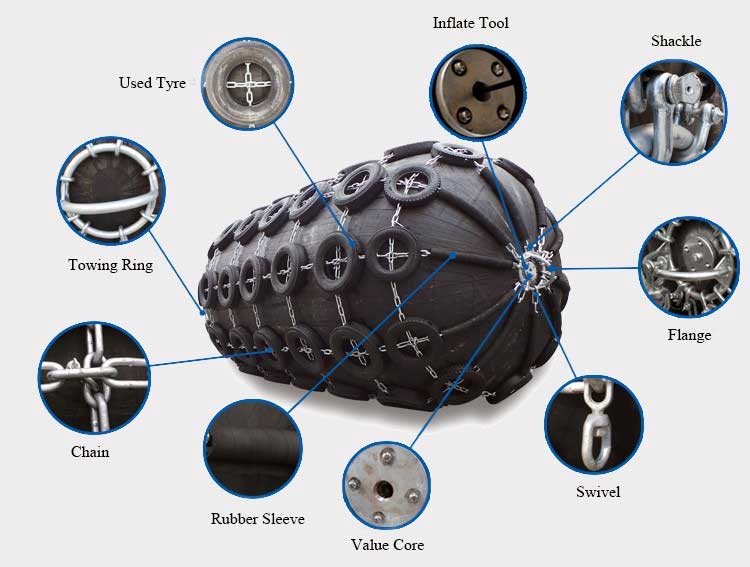

1. Outer rubber layer
The rubber layer covering the outer side of the fender is used to protect the fender frame material and the inner rubber from external damage or wear.
2. Inner rubber layer
The rubber layer on the inner wall of the fender is used to prevent gas leakage and maintain the air pressure of the fender.
3. Cord rubber layer
The baked skeleton material consists of hanging rubber cord fabric.
4. Winding ring
A steel ring placed at one (or both) ends of the fender is used to fix the end of the cord fabric.
5. End flange
The metal parts at both ends of the fender can be fitted with inflatable valves and safety valves.
Advantages of Yokohama Pneumatic Fenders
Yokohama pneumatic fenders have been widely used in tankers, container ships, yachts, offshore platforms, large docks, military ports, large terminals, etc.
Compared with the traditional elastic rubber fenders, Yokohama fenders have the following advantages:
- Large impact energy absorbed and small impact resistance to the ship.
- Easy to install.
- Good elasticity and no deformation under pressure.
- Lightweight, practical and economic.
Performance of Yokohama Pneumatic Fenders
| Diameter x Length [mm] | 50kPa Performance Data | 80kPa Performance Data | ||||
| Hull Pressure at GEA / kN / m2 | Reaction Force /kN | Energy Absorption /kNm | Hull Pressure at GEA / kN / m2 | Reaction Force /kN | Energy Absorption /kNm | |
| 1000×1500 | 122 | 182 | 32 | 160 | 239 | 45 |
| 1000 x2000 | 132 | 257 | 45 | 174 | 338 | 63 |
| 1200 x2000 | 126 | 297 | 63 | 166 | 390 | 88 |
| 1350 x2500 | 130 | 427 | 102 | 170 | 561 | 142 |
| 1500 x 3000 | 153 | 579 | 153 | 174 | 761 | 214 |
| 1700 x 3000 | 128 | 639 | 191 | 168 | 840 | 267 |
| 2000 x 3500 | 128 | 875 | 308 | 168 | 1150 | 430 |
| 2500 x4000 | 137 | 1381 | 663 | 180 | 1815 | 925 |
| 2500 x 5500 | 148 | 2019 | 943 | 195 | 2653 | 1317 |
| 3300×4500 | 130 | 1884 | 1175 | 171 | 2476 | 1640 |
| 3300 x 6500 | 146 | 3015 | 1814 | 191 | 3961 | 2532 |
| 3300 x 10600 | 158 | 5257 | 3067 | 208 | 6907 | 4281 |
| 4500 x 9000 | 146 | 5747 | 4752 | 192 | 7551 | 6633 |
| * Other sizes can be produced following the client’s requirements. | ||||||
Selection of Yokohama Pneumatic Fenders
When ship owners choose fenders, sometimes the factors considered are not comprehensive enough, and they often feel very troublesome. The following example can help solve this problem.
Examples of fender options for small and medium-sized ships
| Tonnage of Vessel (T) | Suitable Size D*L (m) | Vessel Type |
| 50 | 0.5*1.0 | Fishing boat |
| 100 | 0.7*1.5 〜1.07.5 | Fishing boat |
| 200 | L0*L5T2*2.0 | Fishing boat and tugboat |
| 300-500 | 1.2*2.0 〜1.525 | Fishing boat and tugboat |
| 1000 | 1.5*2.5 〜1.5*3.0 | Tugboat, transport vessel |
| 3000 | 2.0*3.0~2.0*3.5 | Ocean trawler, transport vessel |
| 10000 | 20*3.5-2.5*4.0 | Transport ship |
Examples of fender options for large ships
| Vessels (DWT) | Assumed landing speed (M/S) | Effective motion energy (KN.M) | Suitable Size D*L (m) |
| 200000 | 0.15 | 1890 | 3.3*6.5 |
| 150000 | 0.15 | 1417 | 3.3*6.5 |
| 100000 | 0.15 | 945 | 3.0*5.0 |
| 85000 | 0.17 | 1031 | 3.0*6.0 |
| 50000 | 0.1 | 600 | 2.5*5.5 |
| 40000 | 0.2 | 672 | 2.5,5.5 |
| 30000 | 0.22 | 609 | 2.5M.0 |
| 20000 | 0.25 | 525 | 2.5*4.0 |
| 15000 | 0.26 | 425 | 2.5*40 |
| 10000 | 0.28 | 329 | 2.0*40 |
Why Are Pneumatic Fenders Also Called Yokohama Fenders?
What is the difference between pneumatic fenders and Yokohama fenders? Pneumatic fenders or Yokohama fenders are actually two names for the same product. Pneumatic fenders are air-filled rubber fenders (hence the name pneumatic fenders). This type of rubber fender was first developed by Yokohama in 1958. Since then, it has become a widely used fender in shipping and ports.
Yokohama fenders are used for berthing ships in (sea) ports as well as the ships themselves. On ships, fenders are often used in situations where a ship (such as a bunkering vessel) approaches to transfer cargo from one ship to another. In addition, pneumatic fenders are also commonly used in offshore engineering or dredging industries.
Because pneumatic fenders are filled with air, the fenders float like foam or foam-filled fenders. So what is the difference between Yokohama pneumatic fenders and foam filled fenders? Please refer to: The difference between Yokohama pneumatic fenders and foam filled fenders.
Yokohama Pneumatic Fender Types
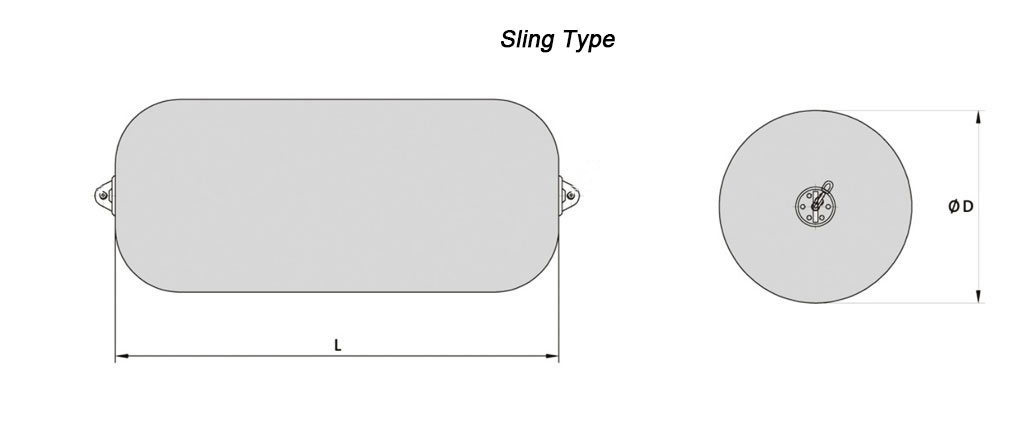
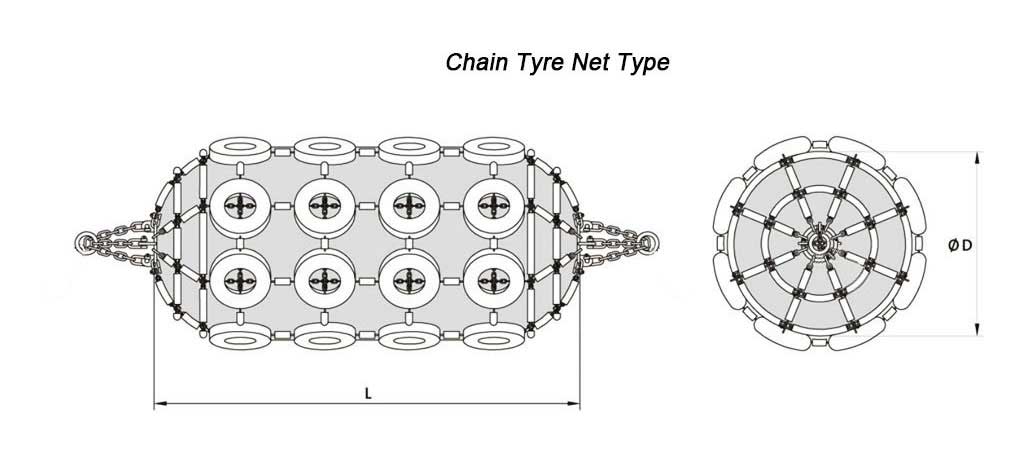
Yokohama pneumatic fenders are available in diameters ranging from 300 mm to 4500 mm and lengths ranging from 500 mm to 9000 mm, as well as special sizes. All sizes are available with sling type or heavy-duty chain and tire mesh.








