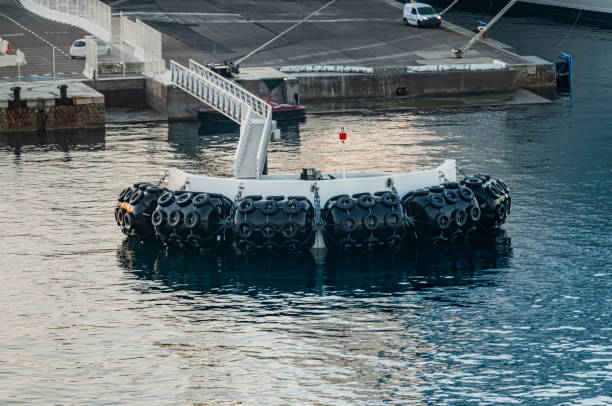
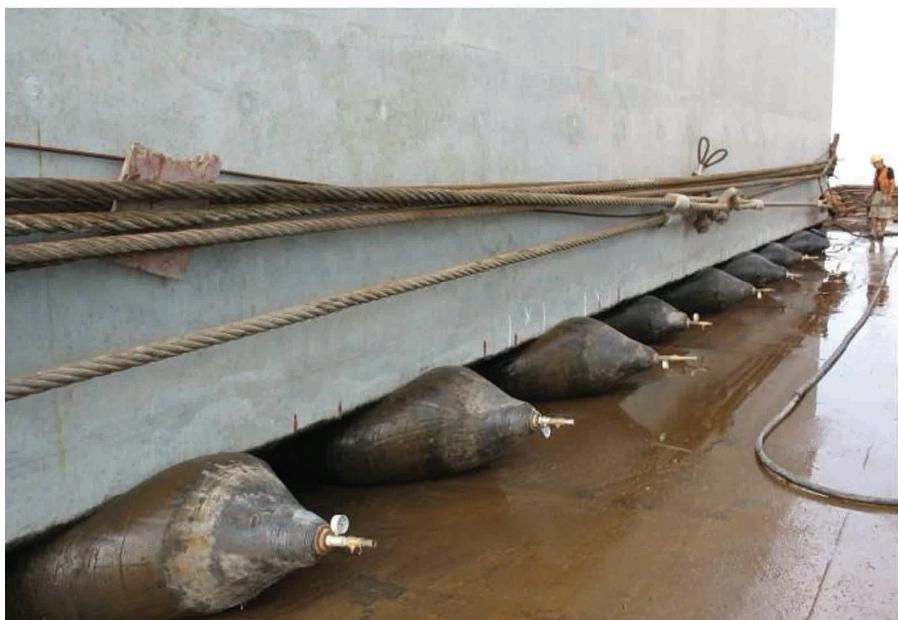
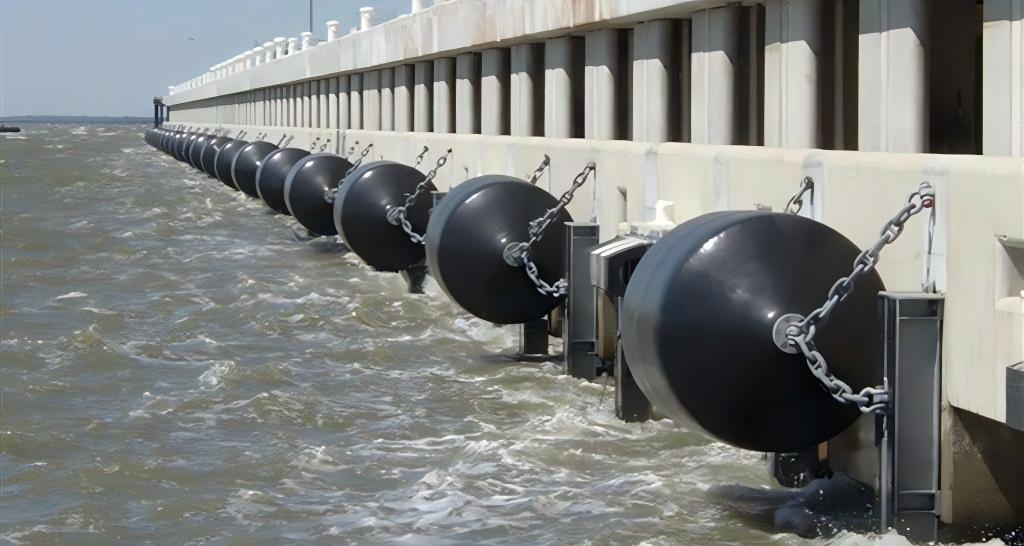
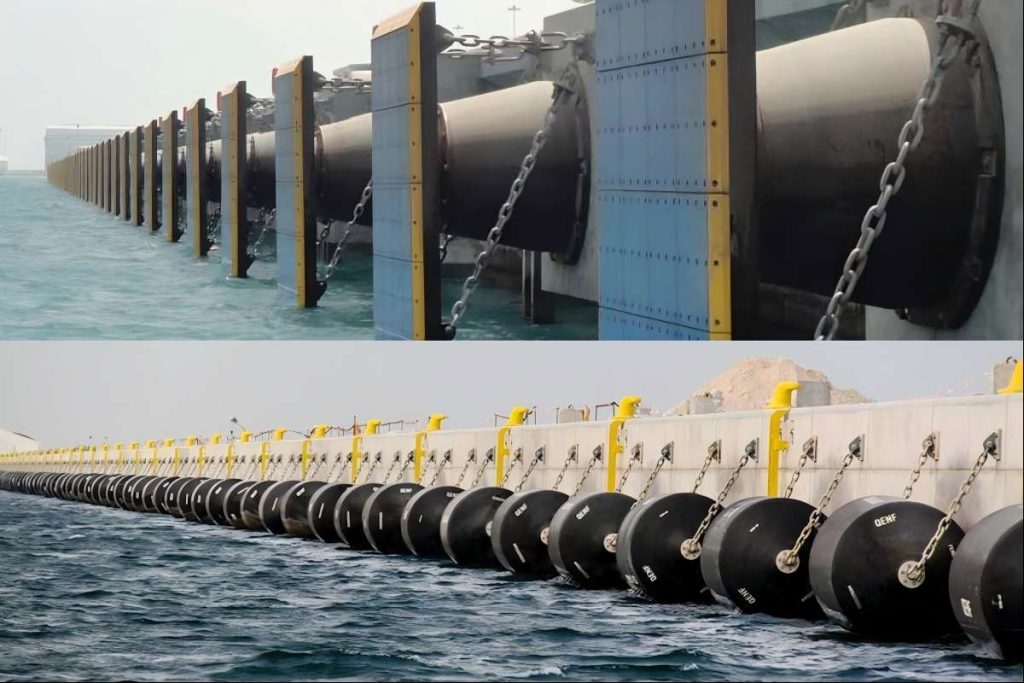
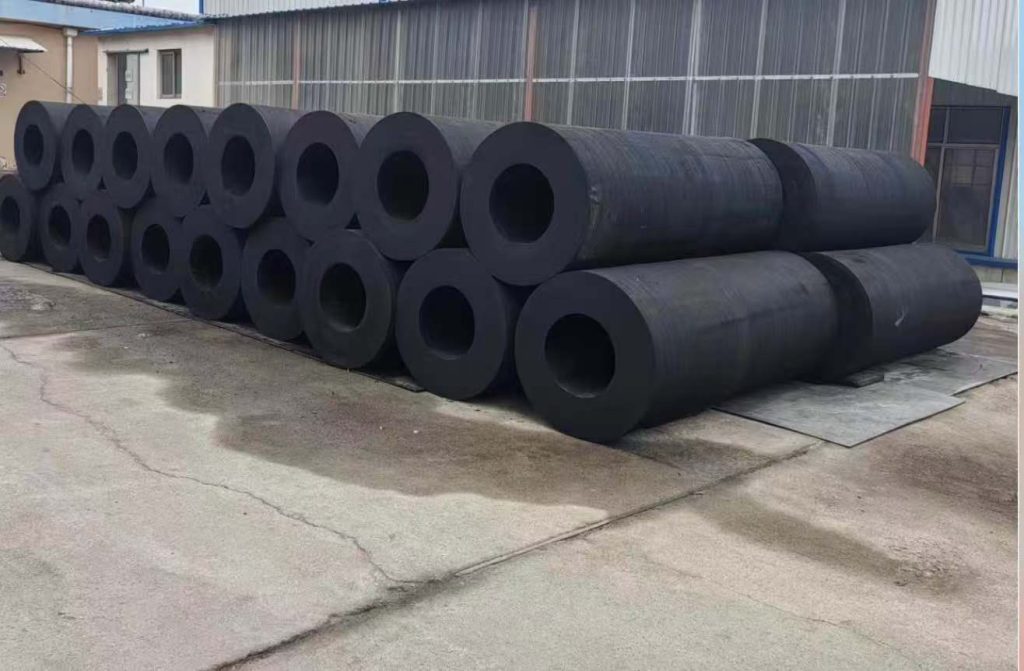
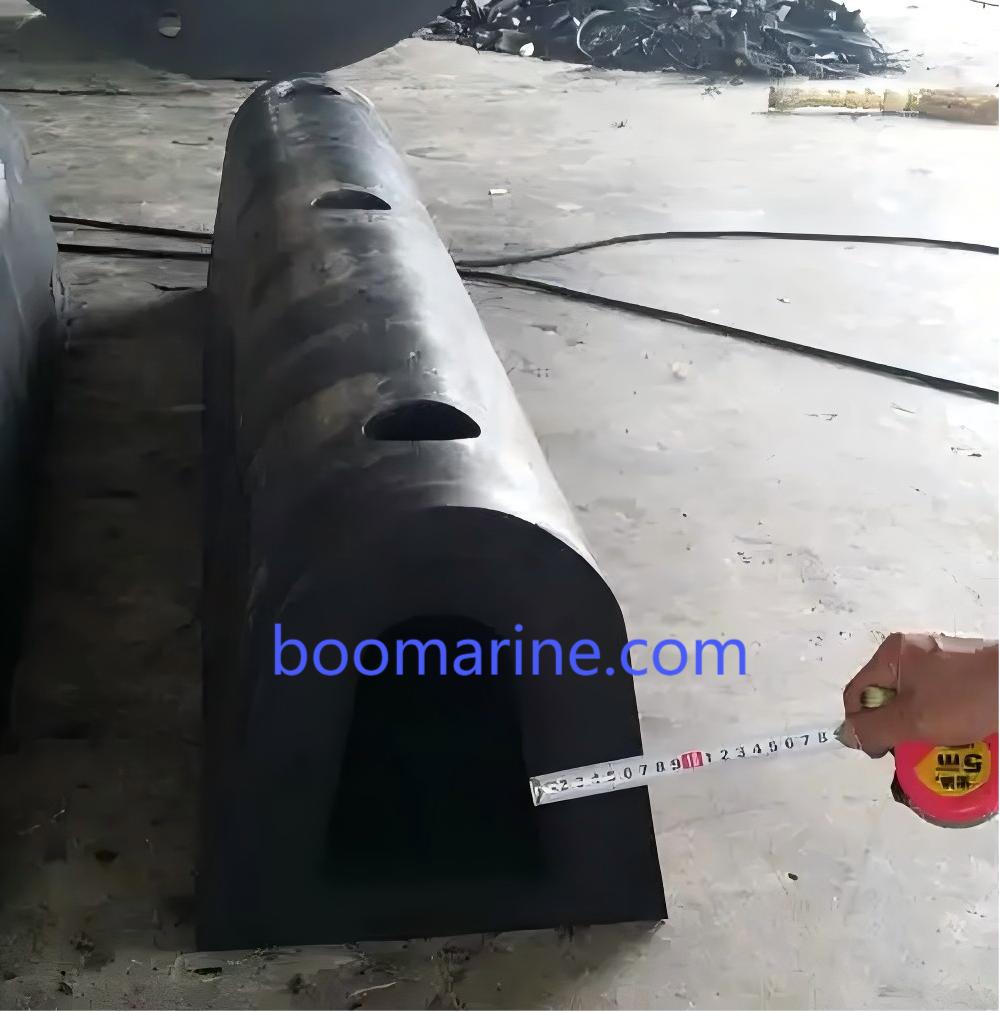
Marine fenders play a crucial role in safeguarding both vessels and docking structures from damage during berthing and mooring operations. These essential components absorb the impact forces generated when a vessel comes into contact with a dock or another vessel. Two primary types of marine fenders dominate the market: Pneumatic rubber fenders and Solid rubber fenders.
This article aims to provide valuable guidance to readers in selecting the most appropriate fender type for their specific marine applications, considering various factors such as vessel size, berthing conditions, and budget constraints.

Understanding the Basics
| Construction | Advantages | Limitations | |
| Pneumatic Rubber Fenders | These pneumatic rubber fenders consist of internal air-filled chambers encased within a robust rubber shell. The air pressure within the chambers plays a crucial role in their energy absorption capabilities. | High Energy Absorption: Due to the compressibility of air, pneumatic fenders offer excellent energy absorption, minimizing impact forces on both the vessel and the dock. | Potential for Air Leaks: The air chambers are susceptible to punctures or leaks, which can significantly reduce the fender’s effectiveness and require timely repairs. |
| Adjustable Pressure: The air pressure within the chambers can be adjusted to fine-tune the fender’s stiffness and reaction forces, allowing for customized performance based on the specific application. | More Complex Maintenance: Regular air pressure checks and potential repairs for leaks necessitate more frequent and potentially complex maintenance compared to solid rubber fenders. | ||
| Low Reaction Forces: Compared to solid rubber fenders, pneumatic fenders generally exert lower reaction forces on the vessel, reducing the risk of damage to the vessel’s hull. | |||
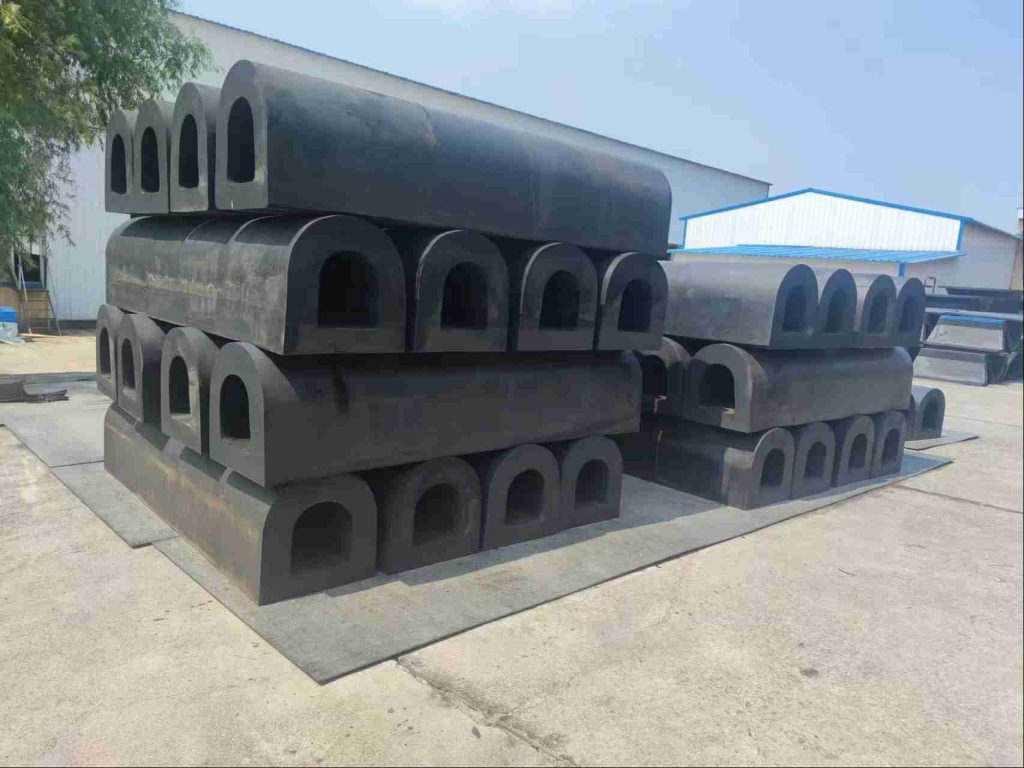
| Solid Rubber Fenders | These fenders are typically made from solid blocks or cylinders of high-quality rubber compounds. | Durable: Solid rubber fenders are known for their exceptional durability and resistance to abrasion, wear, and tear. | Higher Reaction Forces: Compared to pneumatic fenders, solid rubber fenders generally exert higher reaction forces on the vessel, increasing the risk of minor damage to the vessel’s hull. |
| Low Maintenance: Due to their solid construction, they require minimal maintenance, making them a cost-effective option in the long run. | Less Energy Absorption: Due to their inherent stiffness, solid rubber fenders typically offer lower energy absorption compared to pneumatic fenders, especially in situations involving high-impact berthing. | ||
| Reliable Performance: Their consistent performance is unaffected by air pressure fluctuations or potential leaks, providing reliable protection in various marine environments. |
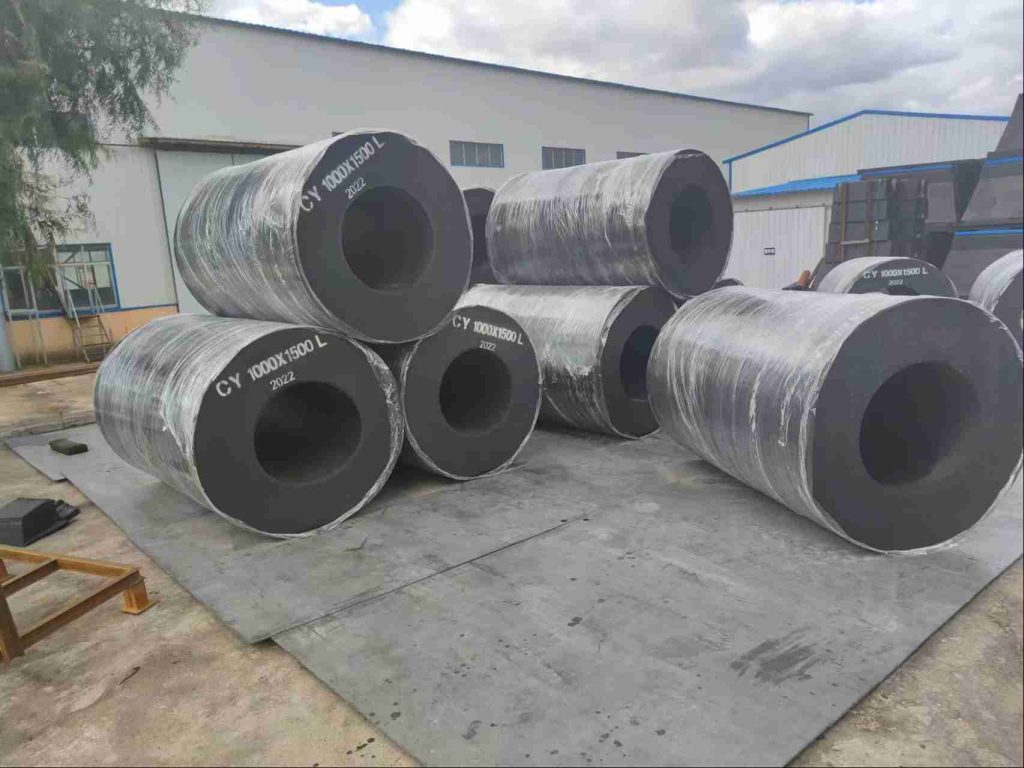

Factors to Consider for Selection
Selecting the most suitable fender system requires careful consideration of several crucial factors:
1. Vessel Type and Size
Vessel Size and Weight: The size and weight of the vessel significantly influence the required fendering system. Larger vessels, such as cruise ships and cargo ships, require more robust and higher-energy absorbing fenders to withstand the greater impact forces during berthing. Smaller vessels, like yachts and fishing boats, generally require less substantial fendering.
Vessel Type: The type of vessel also plays a role. For example, high-speed vessels may require fenders that can withstand greater impact forces and minimize vibrations. Passenger vessels may prioritize comfort and minimize noise and vibration transmitted to the vessel during berthing.
2. Berthing Conditions
Tidal Variations: Significant tidal ranges can create challenging berthing conditions. Fenders must be able to accommodate the changing water levels and prevent the vessel from grounding or colliding with the dock during low tide.
Wave Action: Exposure to waves can generate significant dynamic forces on the vessel during berthing. Fenders must be able to absorb the energy of wave impacts and prevent excessive vessel movement.
Currents: Strong currents can exert significant forces on the vessel, potentially causing it to collide with the dock. Fenders must be able to withstand these forces and maintain a safe distance between the vessel and the dock.
3. Dock/Structure Type
Concrete Docks: Concrete docks are typically rigid and can transfer impact forces directly to the vessel. Fenders for concrete docks should be designed to absorb these forces and minimize damage to both the vessel and the dock.
Steel Docks: Steel docks are generally more flexible than concrete docks, but they can still transmit significant forces during berthing. Fenders for steel docks should be selected to accommodate the flexibility of the structure and minimize the risk of damage.
Floating Docks: Floating docks move with the vessel during berthing, reducing the impact forces. However, fenders are still necessary to prevent excessive movement and protect the vessel from contact with the dock.
4. Budget and Maintenance Considerations
Initial Costs: Pneumatic fenders generally have higher initial costs compared to solid rubber fenders due to the more complex construction and the need for associated equipment (e.g., air compressors, pressure gauges).
Long-term Costs: While initial costs may be higher, pneumatic fenders can offer long-term cost savings due to their potential for lower maintenance requirements in some cases.
Maintenance Requirements:
- Pneumatic Fenders: Require regular air pressure checks, potential for air leaks, and periodic inspections for damage to the rubber casing.
- Solid Rubber Fenders: Typically require minimal maintenance, primarily visual inspections for wear and tear.
5. Safety and Environmental Concerns
Vesel and Crew Safety: Fenders should be designed to minimize the risk of vessel damage, prevent excessive vessel movement, and reduce the risk of injuries to crew members during berthing operations.
Environmental Impacts:
- Pneumatic Fenders: Potential for oil spills in the event of a significant air leak, which can have detrimental environmental consequences.
- Proper disposal: End-of-life disposal of both fender types should be carried out responsibly to minimize environmental impact.
Application Examples
Pneumatic Fenders:
- Ideal for Large Vessels: Due to their high energy absorption capabilities, pneumatic fenders are well-suited for large vessels such as cruise ships, tankers, and container ships, which experience significant impact forces during berthing.
- Berthing in Exposed Locations: In exposed locations with strong waves, currents, and tidal variations, pneumatic fenders can effectively absorb the dynamic forces and minimize vessel movement.
- Situations Requiring High Energy Absorption: Applications involving frequent and high-impact berthing, such as in busy ports and terminals, often benefit from the superior energy absorption of pneumatic fenders.
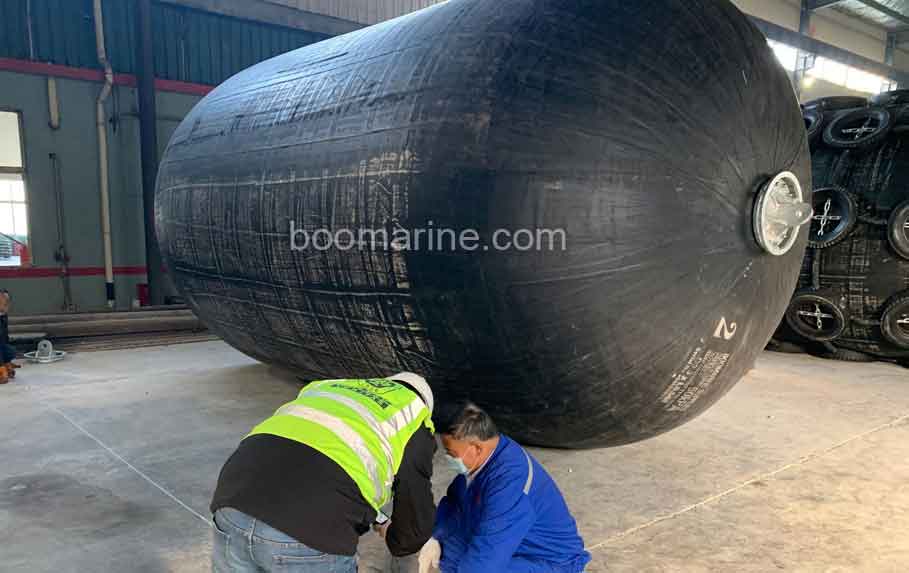

Solid Rubber Fenders:
- Suitable for Smaller Vessels: Solid rubber fenders are a cost-effective and reliable option for smaller vessels such as yachts, fishing boats, and smaller commercial vessels.
- Sheltered Harbors: In sheltered harbors with calm waters and minimal wave action, solid rubber fenders can provide adequate protection with minimal maintenance requirements.
- Applications Where Low Maintenance is Crucial: Due to their simple construction and minimal maintenance needs, solid rubber fenders are ideal for applications where regular maintenance is impractical or costly.
Summary
Selecting the most appropriate marine fender system requires a comprehensive evaluation of several key factors. These include:
- Vessel characteristics: Size, weight, type, and operational profile.
- Berthing conditions: Tidal variations, wave action, currents, and exposure to environmental factors.
- Dock/structure type: Material, rigidity, and flexibility of the docking infrastructure.
- Budgetary constraints: Initial and long-term costs, including maintenance expenses.
- Safety and environmental considerations: Minimizing risk of damage, ensuring crew safety, and minimizing environmental impact.
The optimal fender choice will vary significantly depending on each application’s specific needs and conditions. There is no one-size-fits-all solution. If you still can’t decide whether to choose pneumatic rubber fenders or solid rubber fenders for marine, don’t hesitate to get in touch with fender expert Boomarine for a piece of professional advice.