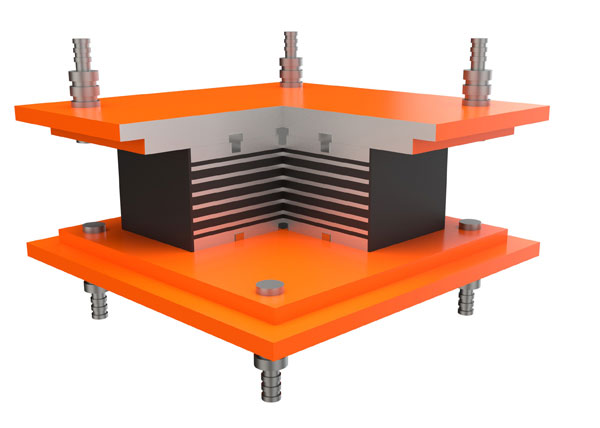
Plain Elastomeric Bearing Pad, also known as non-reinforced elastomeric bearings, is common and economical bearings of elastomers. It is made of neoprene, natural rubber, or polyurethane, and is usually cut from large pieces of rubber, or individually molded into any desired shape. It is typically used in locations where load capacity and thermal movement are limited. It provides a low-cost option for bridges with lighter loads.
Plain elastomeric bearing pads can be used in steel structures, precast concrete structures, standard concrete slabs and any place where vibration isolation is required. It not only allows expansion and contraction of prefabricated or steel components, but also minimizes the impact of structural vibration and absorbs noise. Therefore, bearings of different thicknesses can be applied to various applications in the bridge and construction industries. And compared with tank bearings and spherical bearings, plain elastomeric bearing pads do not have steel plates outside the rubber pads, so they are more suitable for small displacement bridges with simple structures. This type of bearing provides an excellent economical solution for applications where structural movement, longitudinal, lateral and rotation are small.
The elastic bearing pads provided by Boomarine are specially designed for bridge and building construction. We choose the best rubber and steel as our raw materials for manufacturing bridge bearings. All products have undergone strict quality testing to ensure that our products meet or exceed customer expectations.
Rubber Physical Properties
| Technical Index | Natural Rubber (-40℃ – 60℃) | Neoprene Rubber(-25℃ – 60℃) | |
| Hardness(IRHD) | 60±5 | 60±5 | |
| Tensile Strength(MPa) | ≥18 | ≥17 | |
| Elongation at Break(%) | ≥450 | ≥400 | |
| Brittleness Temperature(℃) | ≤ -50 | ≤ -40 | |
| Compression Set(70℃ × 24h)% | ≤ 30 | ≤ 15 | |
| Ozone Aging Resistance(20% strain,40℃ × 96h) | 25 pphm | 100 pphm | |
| No Cracks | No Cracks | ||
| Hot Air Aging | Test Condition(℃ × h) | 70 × 168 | 100 × 70 |
| Max Change in Tensile Strength(%) | – 15 | -15 | |
| Max Change in Elongation at Break(%) | – 20 | -40 | |
| Max Change in Hardness(IRHD) | -5 , +10 | 0 , +10 | |
| Bond Strength Between Elastomer and Steel Plate(KN/m) | ≥10 | ≥10 | |
| Bond Strength Between Elastomer and PTFE(KN/m) | ≥7 | ≥7 | |
Features of Plain Elastomeric Bearing Pad:
- Simple but robust construction.
- Can be individually formed into any desired shape.
- Sufficient vertical stiffness to carry vertical loads.
- Can transfer pressure from the superstructure to the abutment.
- Good elasticity to accommodate the rotation of the girder end.
- Large shear deformation to meet the horizontal displacement of the superstructure.
- Can minimize the impact of structural vibration and absorb noise.
- More economical than steel laminated elastic bearings.
Applications of Plain Elastomeric Bearing Pad:
- Plain elastomeric bearing pads can be used for bridges, viaducts, buildings, storage tanks, sealing elements, isolation, etc.
- It also can be used for steel structures, precast concrete structures, standard concrete slabs and any place where vibration isolation is required.
- Different plane shapes are applicable to different span structures: rectangular bearings for orthogonal bridges; circular bearings for curved bridges, inclined bridges and bridges with cylindrical piers.
- It can be used in combination with complementary bearing devices to expand its application areas, such as temporary or permanent sliding systems, or restraint systems in any direction.

Types of Elastomeric Bearings
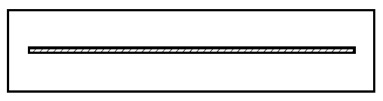
Type A: Laminated bearing fully covered with elastomer comprising only one steel reinforcing plate.
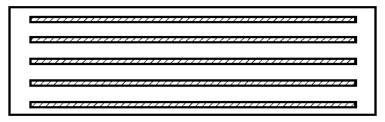
Type B: Laminated bearing fully covers with elastomer comprising at least two steel reinforcing plates.
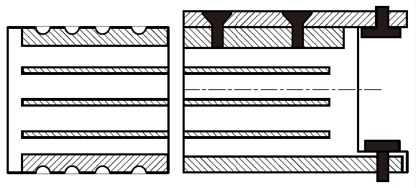
Type C: Laminated bearing with outer steel plates (profiled or allowing fixed).
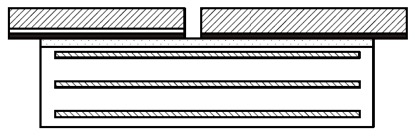
Type D: Type B with PTFE sheet bonded to the elastomer.
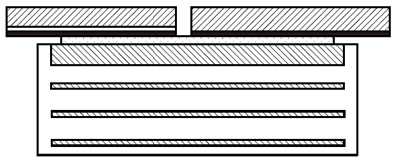
Type E: Type C with one outer plate bonded to the elastomer and PTFE sheet recessed in the steel.

Type F: Plain pad bearing and strip bearings.